Preventive maintenance (PM) is a key part of facilities management, and your goal is to develop and implement consistent practices that improve the performance and safety of the equipment at your facilities. While the implementation of a preventative maintenance plan can be time-consuming and costly, from our years of experience, we believe that the benefits far outweigh the risk of not having one in place. Fewer equipment stops mean less production waste, less unplanned downtime, and a healthier business. Follow these five tips to ensure you have an effective, efficient, and sustainable PM program for your facility.
- Blog
Top 5 Preventative Maintenance Tips
Preventive maintenance (PM) is a key part of facilities management, with the goal of any successful program being to develop and implement consistent practices that improve the performance and safety of the equipment at your facilities. While the implementation of a preventative maintenance plan can be time consuming and costly, from our years of experience, we believe that the benefits far outweigh the risk of not having one in place. Follow these five tips to ensure you have an effective, efficient and sustainable PM program for your facility.
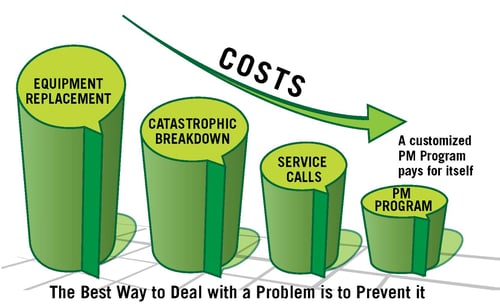
source:https://www.robertgibb.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/preventive-maintenance-graph-horizon_revised.jpg
#1 Have a plan for plant maintenance
If you have a plan, dust it off, revive it, and stick to it. Depending on which study or industry you research, the average rate of return is 7:1 to 35:1 for each PM dollar spent. Can you afford not to spend the time and resources to perform a PM with those numbers?
If you don’t have a plan, develop one. Even the most basic plan is better than no PM plan at all. A simple way to start is to document the system components and divide them into weekly, monthly, and/or quarterly inspection timelines.
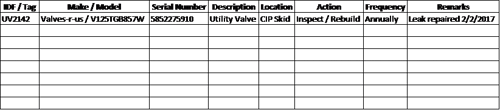
Document the results and findings on the PM plan. You will soon gather enough data to determine, based on wear and performance of the components, when you required to perform maintenance on the system. With this date, you can predict component issues and more reliably prevent the issues and their negative impact on operations.
#2 Get the component manual and have the team review it
Some component manufactures outline guidelines and timelines for PM tasks. Read the manufacturer guidelines, as well as the warranty conditions to help you figure out the best tasks for preventive maintenance. For those that don’t, documenting your findings, as mentioned above, will help define your own timeline. Regardless of the timeline, most manufactures’ manuals will have simple maintenance tasks outlined that will help increase the performance and life expectancy of their components.
#3 Conduct visual and physical inspections
Why do pilots perform pre-flight walkarounds? To identify and correct obvious issues before they start the journey. The same can apply to you and your team! Visually and physically inspecting the system and components both when idle and during operation allows you monitor the system, looking for the most obvious issues. Correct the issue, document them on your PM plan, and determine the mean time before failure on your PM plan as well. You’ll save time and money correcting issues before hand rather than dumping product to drain or having unscheduled production downtime.
#4 Keep your operation running as efficiently and effectively as possible
Test, adjust, and/or calibrate components in accordance with the manufactures recommendation or at a minimum, quarterly, or semi-annually, depending on use and operating conditions. Train your team on the intricacies of the calibration process or hire subject matter experts to keep your operation running smoothly.
#5 Keep the equipment and components clean, dry, and serviceable
Along with the PM tips outlined above, ensuring your system and components are operating in the environment in which they were designed to operate. Water, grease, product, or foreign material inside a component that isn’t designed to have foreign material in will decrease its life expectancy and decrease its operating capabilities.


